- 0224 451 74 34
- 0532 214 02 80
- info@zeynepkirker.com
Skin is the largest organ of the body and forms a wall to protect body from the outer world.
Skin protects the body against mechanic, chemical and biological factors, regulates fluid balance and body temperature. Skin is an organ which conducts sensations like touching, pressure, temperature and pain. Sensations of fair people may be observed through the skin when their skin gets red or pale. Skin is also associated with immunity processes and has metabolic functions (synthesis vitamin D and cholesterol).
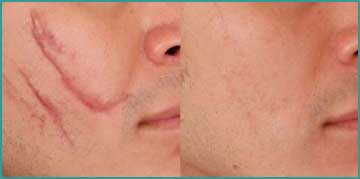
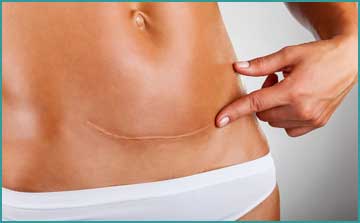
Wound is the injury or destruction of the tissue so as to interrupt normal functions. The natural reaction of the organism is to heal the wounds as soon as possible and maintain the normal functions. This process is defined as “wound healing”. Wound healing follows the same biological and biochemical principles in all tissues.
Primary wound healing is the optimum type of wound healing. Borders of the wound should be regular and aligned; the wound should be clean and well dressed. Primary wound healing results in rapid and uncomplicated closure of the wound without inflammation within 4-6 days. Little crusting occurs and structure and function of the tissue rapidly returns to normal.
Secondary wound healing occurs when tissue loss, alignment disorder, infection or insufficient blood supply is present. Secondary wound healing takes longer than one week and detected as a delayed wound healing which does not exceed 2-3 weeks.
Wound cleaning is widely used for management of delayed wound healing. Some enzymatic, antimicrobial, physical and surgical cleaning techniques may be used. Working under hygienic conditions, prevention of inappropriate dressing and stopping wound drying are important.
Enzyme preparations are among the mainstay of wound healing. Enzymes contribute to physiologic wound cleaning through selectively degrading the necrotic material and the crust in exudative phase and thereby new tissue formation (granulation and epithelization) is accelerated. One of the most important advantages of cleaning with enzyme is separation of necrotic tissue while the healthy tissue is preserved.
Natural collagen is the most important connective tissue protein and the most important structure of the skin. Human collagen is composed of parallel tropocollagen molecules arranged differently according to tissue type.
Tropocollagen which is the main component of collagen is composed of triple helix.
Each polypeptide is mainly composed of aminoacids, glycine, hydroxyproline and proline. These components form a triple helix which begins with glycine.
Collagenase is the only enzyme which can degrade collagen. Endogenous collagenases are released into the wound by fibroblasts, keratinocytes, macrophages and granulocytes which migrate during the exudative phase of wound healing. Afterwards collagenase breaks collagen fibers into smaller pieces which may be degraded more by proteases. Very small collagen degradation products act as chemotactic factor for chemotaxis of granulocytes and macrophages. Granulocytes and macrophages continue wound cleaning process through phagocytosis. Macrophages also secrete biologically active substances like collagenases which accelerate granulation (proliferative phase). Collagen activity decreases for prevention of cell proliferation when new granulation tissue is formed. Endogenous collagenase is deficient in wounds which heal late. This means that the necrotic tissue which is bound to wound base with collagen fibers could not be sufficiently degraded.
Use of bacterial collagenase preparations is recommended for the patients whose wounds heal late as endogenous collagenase increases activity and accelerates healing.
Bacterial growth occurs in all wounds which heal late. However this does not indicate the presence of an infection which requires treatment. Therefore antibiotics should only be used in presence of >105/mm' colony forming bacterial growth, redness, pain, purulent wound, and systemic findings like fever.
Escherichia Coli, Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Streptococ are among the most common infectious agents in wound infections.
Antibiotics may be used systemic or locally. Local use of antibiotics may lead to problems like resistance to antibiotics or contact allergy. It is difficult to reach sufficient drug concentration without harming wound healing process. Local therapy does not lead to systemic side effects.
Antiseptics may be used instead of antibiotics due to the risk for sensitivity.
It should be kept in mind that effect of antiseptics may be low, they may lead to sensitivity although not high as antibiotics and impair wound healing process.
Physical measures may be used for removal of necrotic tissue and wound cleaning. Wet dressing is one of them. Ringer lactate is the best selection as it does not impair electrolyte balance and wound healing process. Washing with H2O2 and irradiation with UV-C light may also be used.
Surgical cleaning is another option for the wounds which heal late. Foreign body, necrosis, crust and poorly dressed tissue may easily be removed surgically. Infection sites may be removed and drainage may be provided for elimination of secretion. However surgery may be associated with infection risk, hemorrhage and pain risk despite the absence of the risk for harming the fresh granulation tissue. Surgical removal should certainly be performed by educated staff.
Recurrent or difficultly healing wounds are usually seen among diabetics. Pressure wounds related with staying in bed and wheel chair for a long time; varices –related wounds; arterial diseases-related wounds; radiation-related wounds may be treated. Treatment processes vary depending on the cause.
Diabetes harm vascular and nerve tissues, and wounds develop particularly in feet. Small traumas in feet may not be recognized and wounds may easily develop. Circulation is insufficient in wound site. Wound rapidly enlarges and become infected. Wound development makes the control of diabetes difficult and thereby makes wound healing impossible. Therefore plasma glucose should be under control, antibiotic should be used in case of infection, necrotic tissues should be removed. The affected leg should be kept above heart level. It should be kept in mind that treatment of foot ulcers of diabetic patients make take a long time. Sometimes amputation may be required.
Wounds which begin with redness in contact site and which may enlarge unless treated may develop in patients who are dependent to bed or wheel chair for a long time. Pressure wound is the most commonly used terminology for these wounds. Elimination of etiologic factors is of great importance for treatment and prevention. Lying and sitting positions of the patients should frequently be changed, pressure sites should be dry and clean, air bed should be used. Progression of the wound may be stopped, treatment may be started and the patient may be prepared for the operation. Pressure wound may be closed with varying techniques depending on the depth and size of the wound. Measures should be taken for healing and prevention of recurrence.
Arteries carry the oxygenized blood to tissues. These vessels are obstructed in diseases like Burger and atherosclerosis, the course of the disease is worse in smokers. Legs may sometimes be cold and painful. Leg ulcers are usually deep in these patients. Toes or legs may undergo amputation in advanced cases. Prevention is of great importance for these patients. Wound healing takes a long time.
They develop in patients who undergo radiotherapy due to cancer. Rarely radiation accidents may be seen. They difficultly heal. Blood circulation is severely impaired due to harmed vessels in radiation site.
Low energy lasers may be used for accelerating wound healing and relieving pain in some chronic diseases.
Experimental studies have indicated that low energy lasers lead to fibroblast proliferation which has great importance in wound healing, increase blood flow and collagen fibers, wound contraction (lessening of wound size through contraction).
Although soft laser treatment is not as effective as the known surgical methods or other methods, it may yield quite positive effects on wound healing as an additional therapy.
Sufficient outcomes may be obtained with low energy lasers in venous wounds for which surgical options and other methods are insufficient.
Low energy lasers may be effectively used through their circulation-increasing effect and positive effects on wound healing in patients who have high operation risk.
Low energy lasers may be used an adjuvant therapy method in rheumatic pain, Raynaud phenomen and cartilage healing.
